The Hyperloop Explained: Re-inventing How We Travel In The 21st Century Using Magnetic Levitation &…
There have been certain inventions that were previously inconceivable and considered ludicrous, that were invented at the turn of the last…
There have been certain inventions that were previously inconceivable and considered ludicrous, that were invented at the turn of the last century that have forever revolutionized how we travel from one place to the other.
At the turn of the 20th century, the airplane, invented by the Wright brothers and the previously invented railroad system that pioneered & ushered in the industrial revolution, changed the way humanity got from one place to the other and laid out the roadmap for the future.
Today we hardly bat an eyelid at how we travel from one country to the other by airplanes. But this was inconceivable back in the 1890s.
Now at the turn of the new decade of the 21st century i.e. as 2020 turns into 2021 and 2022, there’s a new kind of technology that will revolutionize how we travel and commute, at the fraction of time, at a much faster speed, and with no carbon emissions that aircrafts and trains usually produce.
That technology is the Hyperloop.
What Is The Hyperloop?
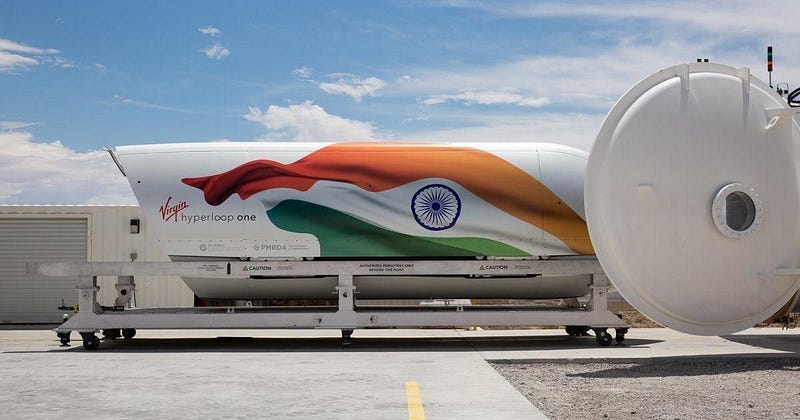
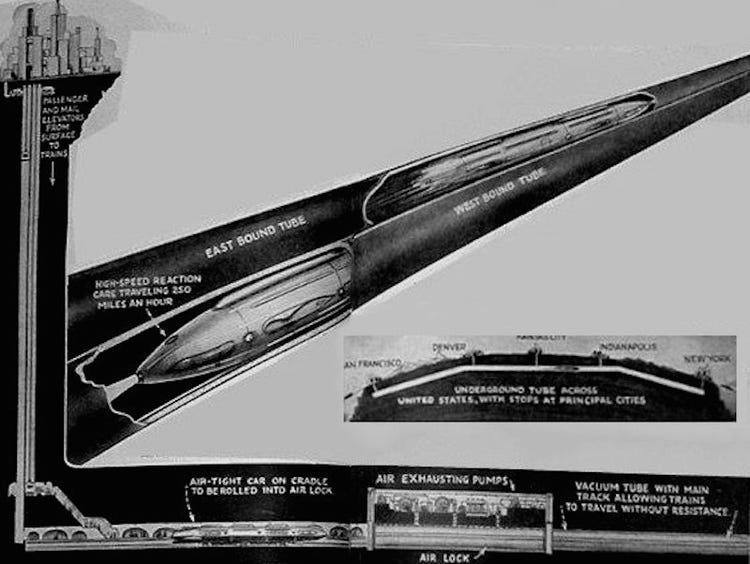
The Hyperloop is a transit system that has a vehicle called a pod inside of a tube about the same size as a subway tunnel, where it sucks most, but not all of the air out of it, using magnetic levitation to propel the pod, making it the equivalent of flying at around 200,000 feet of altitude .
This allows the pod to glide at airline speeds, without turbulence, for a fraction of the energy consumption, i.e. about one tenth, of an aircraft, to be precise.
A Hyperloop system can transform short-haul journeys and commutes from hours to minutes & this can all be done without harmful greenhouse emissions that current methods of transport entail.
History
While this may seem like a modern concept it was, in fact, envisioned shortly after the Wright brothers successfully made their first flight in the early 20th century.
A year after the Wright brothers’ historic first flight, an inventor, an American physicist named Robert Goddard, proposed an entirely new form of transportation: the vac train or the vacuum train.
He envisioned a high-speed mass transit system where people would travel on the ground, with little to no air resistance, inside of a tube. And today, these are some of the earliest renderings of what we call the Hyperloop.
The idea for the Hyperloop was promoted first by Elon Musk back in 2013 when he published a paper called the “Hyperloop Alpha” white paper. It sketched out an idea with an open invitation for anyone to take it from a concept and design it to reality.
The Problem & Breakthrough
Josh Giegel, an engineer from Los Angeles, read Elon Musk’s paper in 2013 and decided to quit his job to make the Hyperloop a reality. He was optimistic but faced a lot of uncertainty and problems during those initial years, as he recounts
“I thought I was being optimistic. My wife, on the other hand, thought I was completely delusional. Either way, we heard over and over that building a functional Hyperloop was unrealistic. But for each “no” we heard, we dove deeper and deeper into the science and the engineering and showed that it was in fact possible, but it was going to be no easy feat for us to build something that had never existed.”
“So our early prototypes started with the traditional concept that maglev(magnetic levitation) uses, that is, where the track controls the vehicle. But something about that just wasn’t quite right for a Hyperloop system.”
“So for months, I had been noodling on how to make our system future-proof. And while I was on a bike ride in the mountains above Los Angeles, I came around a bend. A 1933 Ford Roadster followed by a Tesla Model S passed me. Those two cars are light-years different in technology, yet they drive on the same passive road. And there it was. Smart vehicle, dumb road. Or in the case of a Hyperloop, smart pod, dumb tube. So technology has made it possible that a car can be modular, upgradeable and future-proof, while the road stays pretty much the same. So for a Hyperloop, our tube is passive and simple, like the road, but our modular pods can evolve as technology advances, just like the automobile.”
The Hyperloop: Using State Of The Art Technology
The Hyperloop is by far the most futuristic mode of transportation that is being tested at the moment. It uses state-of-the-art tech that pushes the frontiers & boundaries of technology far into the future, and as Giegel accounts:
“Our mission that we’ve chosen to accept is to build the world’s largest vacuum structures, devise new passive magnetic guideways, create pods capable of withstanding a space environment, powered by next-generation batteries while levitating using state-of-the-art magnetic levitation, while quietly accelerating, using the world’s most efficient linear electric motor.”
You can read more about the technology used by the Hyperloop in this article.
Where We’re At With The Hyperloop Today
Giegel and the employees at his company have made leaps and bounds of progress since he first quit his job in 2013 after reading Elon Musk’s paper. As he recounts:
“After building that system, we created a test track in the desert outside of Las Vegas. We’ve operated the system over 500 times and had countless other tests on our subsystems.”
“But there was one test that was going to be the defining moment for Hyperloop technology: the first passengers in the vehicle. And we were going to do it with regular people that didn’t need years of training and experience to set foot inside of a space capsule.”
“So by October of 2020, we had run hundreds of tests. We had an independent safety auditor give us the green light, but still, it was nerve-racking.”
“And on November 8th, 2020, we made our first attempt. So at our test site, my colleague Sara and I climbed into that can-like vehicle suspended by magnetic levitation at a near-vacuum environment, and the countdown began.”
“In those 15 seconds, we showed the world that what was deemed ludicrous over 100 years ago was in fact possible. That brief moment has opened so many doors for us. We’ve had conversations in the US, Europe, India, the Middle East, about building Hyperloop systems in the next 10 years. This is the start of a systemic change in the way we travel.”
The Hyperloop has been approved in India as of 2018 and has been set to be constructed between Mumbai and Pune reducing the travel time from 3–4 hours to only 30 minutes, as shown in this video:
As of 2022, tests are ongoing and now a handful of companies around the world are working with governments in different countries on making the Hyperloop a reality by 2030.
No Carbon Emissions
As countries around the world are looking at ways of reducing carbon emissions significantly because of the severity of the pertinent issues such as climate change and global warming that the world is grappling with in the 21st century, the Hyperloop, by its conception and design is set to categorically change the way we travel with no greenhouse emissions and reducing travel time considerably.
The Future
With humankind’s constant fascination with speed and how the roadmap of the future is being set with technology such as the Hyperloop, what now takes us hours of commute by conventional modes of transport, will change to only minutes.
Giegel and his company, and other companies around the world are working hard everyday on perfecting the Hyperloop, so that it becomes a reality for everyday transit.
It is, in its design & execution, the seemingly next step in the evolution of transportation for the human race.
As Giegel says,
“My hope for a Hyperloop system is that it can transform the way that we live — we can live where we want to live, work where we want to work, we can create a world in which your daughter, who lives in Los Angeles, can go surfing in Santa Cruz and be home in time for lunch. A world in which 150 million people can live in Mumbai and travel to Pune, the equivalent distance of Philadelphia to New York, in 30 minutes, not four hours, while saving 1.1 million tons of pollution each and every year.”
“The last century started with two people riding on a plane, and it ended with millions of people flying all over the world. This decade started with two people riding on a hyperloop system, and my hope is that by the end of it, you’ll ride one too.”
In his TED Talk, published in August 2021, Josh Giegel, co-founder and CEO of Virgin Hyperloop, explains how he & the hundreds of employees in his company are trying to revolutionize how the human race travels for the foreseeable future using the Hyperloop.